Who was the plaintiff in Brown v . Board of Education?
Mar 29, 2022 · As the first white attorney for the NAACP, Jack Greenberg helped to argue Brown v. Board of Education at the U.S. Supreme Court level. Bolling v. Sharpe. U.S. District Court, Washington, D.C.
What was the decision of Brown v . Board of Education?
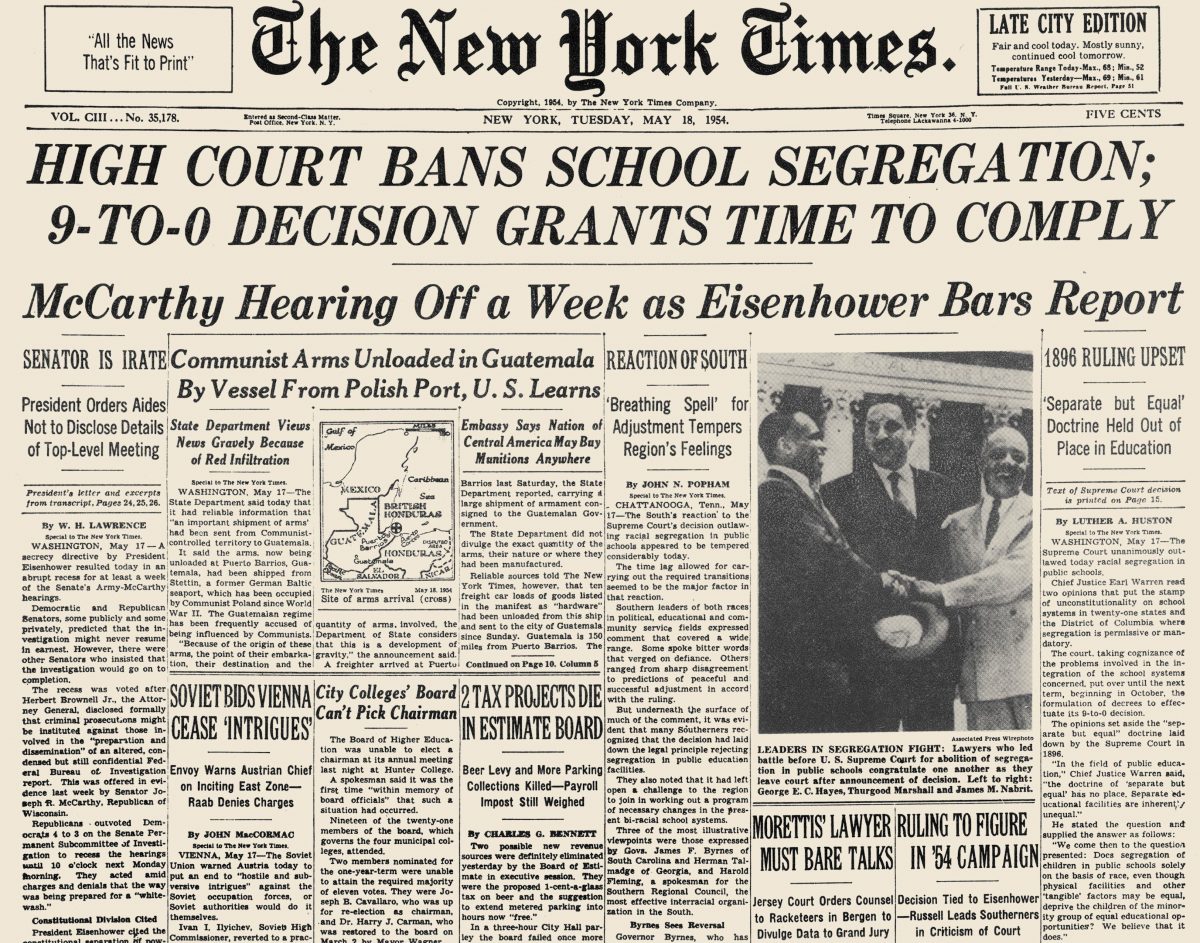
The U.S. Supreme Court case, Brown v. Board of Education, was bundled with four related cases and a decision was rendered on May 17, 1954. Three lawyers, Thurgood Marshall (center), chief counsel for the NAACP’s Legal Defense Fund and lead attorney on the Briggs case, with George E. C. Hayes (left) and James M. Nabrit (right), attorneys for the Bolling case, are shown standing …
Who was Brown in Brown v Board?
Jun 19, 2020 · 4.7/5 (532 Views . 37 Votes) The U.S. Supreme Court case, Brown v. Board of Education, was bundled with four related cases and a decision was rendered on May 17, 1954. Three lawyers, Thurgood Marshall (center), chief counsel for the NAACP's Legal Defense Fund and lead attorney on the Briggs case, with George E. C. Hayes (left) and James M.
What kind of lawyer handles lawsuits against schools?
Jun 08, 2021 · The NAACP and Thurgood Marshall took up Brown’s case along with similar cases in South Carolina, Virginia, and Delaware as Brown v. Board of Education. Oliver Brown died in 1961. Robert L. Carter Born in 1917, Robert Carter, who served as an attorney for the plaintiffs in Briggs v. Elliott, was of particular significance to the Brown v. Board of Education case because …
Who was the lead attorney in the Brown v Board of Education case?
Supreme Court case, Brown v. Board of Education, was bundled with four related cases and a decision was rendered on May 17, 1954. Three lawyers, Thurgood Marshall (center), chief counsel for the NAACP’s Legal Defense Fund and lead attorney on the Briggs case, with George E. C. Hayes (left) and James M. Nabrit (right), attorneys for the Bolling case, are shown standing on the steps of the U.S. Supreme Court congratulating each other after the Court’s decision declaring segregation unconstitutional.
When was Brown v. Board of Education?
Attorneys for Brown v. Board of Education, May 17, 1954
Why was Brown v. Board of Education important?
This grouping of cases from Kansas, South Carolina, Virginia, the District of Columbia, and Delaware was significant because it represented school segregation as a national issue, not just a southern one. Each case was brought on the behalf of elementary school children, involving all-Black schools that were inferior to white schools.
Who was the dean of Howard University in the Brown v. Board of Education case?
Their case eventually became one of five included in the landmark 1954 case, Brown v. Board of Education. Spottswood W. Robinson, III, who was born in 1916, taught law at Howard University, in Washington, DC, and eventually became dean of the school. He made his mark on the history of Brown v.
What was the Bolling case?
Although Bolling is historically considered one of the Brown v. Board of Education bundle cases, it was a different case due to the legal arguments.
What was the precedent in Ferguson v. Brown?
Ferguson ruling of the United States Supreme Court as precedent. The plaintiffs claimed that the "separate but equal" ruling violated the equal protection clause of the 14th Amendment. In 1954, the Supreme Court unanimously ruled in Brown v.
Who was the plaintiff in the Belton v. Gebhart case?
Ethel Louise Belton#N#Ethel Belton and six other adults filed suit on behalf of eight Black children against Francis B. Gebhart and 12 others (both individuals and state education agencies) in the case Belton v. Gebhart. The plaintiffs sued the state for denying to the children admission to certain public schools because of color or ancestry. The Belton case was joined with another very similar Delaware case, Bulah v. Gebhart, and both would ultimately join four other NAACP cases in the Supreme Court ruling in Brown v. Board of Education. Belton was born in 1937 and died in 1981.
Who was the Supreme Court Justice in Kansas?
Fatzer served as Kansas Supreme Court Justice from February 1949 to March 1956. Jack Greenberg. Jack Greenberg, who was born in 1924, argued on behalf of the plaintiffs in the Brown v. Board of Education of Topeka case, and worked on the briefs in Belton v. Gebhart.
Who was the lead defendant in Bolling v. Sharpe?
C. Melvin Sharpe , acting as President of the Board of Education of the District of Columbia from 1948 to 1957, was named as the lead defendant in the case Bolling v. Sharpe. Earl Warren. Chief Justice Earl Warren, who was born in 1891, secured a unanimous decision in Brown v.
What was the landmark decision in the case of Brown v. Board of Education?
Board of Education of Topeka, Kansas, the U.S. Supreme Court declared state laws establishing separate public schools for students of different races to be unconstitutional.
What was the effect of Brown vs Board of Education on the South?
The decision in Brown v. Board of Education forced the desegregation of public schools in 21 states and intensified resistance in the South, particularly among white supremacist groups and government officials sympathetic to the segregationist cause. In Virginia, U.S. Senator Harry F. Byrd, Sr. started the Massive Resistance movement, which sought to pass new state laws and policies as a means of keeping public schools from being desegregated. In one of the most notorious instances of resistance to the decision, Arkansas Governor Orval Faubus called out the National Guard in 1957 to keep black students from entering Little Rock Central High School.
How many families were involved in the Topeka class action lawsuit?
n 1950, the Topeka Chapter of the National Association for the Advancement of Colored People (NAACP) organized another case, this time a class action suit comprised of 13 families.
When did the NAACP appeal to the Supreme Court?
The plaintiffs appealed to the U.S. Supreme Court in 1952 and were joined by four similar NAACP-sponsored cases from Delaware, South Carolina, Virginia, and Washington, D.C.
Which amendment prohibited the operation of separate public schools based on race?
The Justices decided to rehear the case in the fall with special attention paid to whether the 14th Amendment's Equal Protection Clause prohibited the operation of separate public schools based on race.
When did black parents start filing court challenges in Kansas?
African American parents in Kansas began filing court challenges as early as 1881. By 1950, 11 court challenges to segregated schools had reached the Kansas State Supreme Court. None of the cases successfully overturned the state law.
When did Warren support Mexican students?
Warren had supported the integration of Mexican-American students in California school systems in 1947, after Mendez v. Westminster and when Brown v. Board of Education was reheard, Warren was able to bring the Justices to a unanimous decision. On May 14, 1954, Chief Justice Warren delivered the opinion of the Court, stating, "We conclude that, ...
What was the Brown v Board of Education case?
Board of Education (1954) was a landmark U.S. Supreme Court decision that struck down the “Separate but Equal” doctrine and outlawed the ongoing segregation in schools. The court ruled that laws mandating and enforcing racial segregation in public schools were unconstitutional, ...
Which court case did the Browns win?
However, the U.S. District Court for the District of Kansas ruled against the Browns, justifying their decision on judicial precedent of the Supreme Court's 1896 decision in Plessy v.
What was the significance of Brown v. Ferguson?
This decision led to more integration in other areas and was seen as major victory for the Civil Rights Movement. Many future litigation cases used the similar argumentation methods used by Marshall in this case. While this was seen as a landmark decision, many in the American Deep South were uncomfortable with this decision. Various Southern politicians tried to actively resist or delay attempts to desegregated their schools. These collective efforts were known as the "Massive Resistance," which was started by Virginia Senator Harry F. Byrd. Thus, in just four years after the Supreme Court’s ruling, the affirmed its ruling again in the case of Cooper v. Aaron, that government officials had no power to ignore the ruling or frustrate and delay desegregation.
What did the Brown II ruling say about segregation?
Nonetheless, since the ruling did not list or specify a particular method or way of how to proceed in ending racial segregation in schools, the Court's ruling in Brown II (1955) demanded states to dese gregate "with all deliberate speed.".
When did the Oliver Brown case start?
The events relevant to this specific case first occurred in 1951, when a public school district in Topeka, Kansas refused to let Oliver Brown’s daughter enroll at the nearest school to their home and instead required her to enroll at a school further away. Oliver Brown and his daughter were black.
Which amendment is the Supreme Court ruling on separate educational facilities?
The Supreme Court’s decision was unanimous and felt that " separate educational facilities are inherently unequal ," and hence a violation of the Equal Protection Clause of the Fourteenth Amendment of the U.S. Constitution.
Who was the chief attorney for Brown v. Board of Education?
Board of Education of Topeka . Thurgood Marshall, the head of the NAACP Legal Defense and Educational Fund, served as chief attorney for the plaintiffs.
Who was the plaintiff in the Brown v. Board of Education case?
In the case that would become most famous, a plaintiff named Oliver Brown filed a class-action suit against the Board of Education of Topeka, Kansas, in 1951, after his daughter, Linda Brown, was denied entrance to Topeka’s all-white elementary schools.
What states acted in accordance with the verdict?
While Kansas and some other states acted in accordance with the verdict, many school and local officials in the South defied it. In one major example, Governor Orval Faubus of Arkansas called out the state National Guard to prevent Black students from attending high school in Little Rock in 1957.
What was Jim Crow's law?
The ruling constitutionally sanctioned laws barring African Americans from sharing the same buses, schools and other public facilities as whites —known as “Jim Crow” laws —and established the “separate but equal” doctrine that would stand for the next six decades.
When did Brown v. Board of Education of Topeka come to the Supreme Court?
When Brown’s case and four other cases related to school segregation first came before the Supreme Court in 1952, the Court combined them into a single case under the name Brown v. Board of Education of Topeka .
When was the Separate But Equal doctrine first ruled?
Separate But Equal Doctrine. In 1896, the Supreme Court ruled in Plessy v. Ferguson that racially segregated public facilities were legal, so long as the facilities for Black people and whites were equal.
Who replaced Vinson in Brown v. Board of Education?
But in September 1953, before Brown v. Board of Education was to be heard, Vinson died, and President Dwight D. Eisenhower replaced him with Earl Warren, then governor of California.
Popular Posts:
- 1. how to get a lawyer for a person in prison
- 2. how to research your lawyer
- 3. how do you look up a lawyer
- 4. where us lincoln lawyer set
- 5. who was my lawyer in a devoce
- 6. what do i need to be an immigration lawyer in new york
- 7. what is lawyer client privilege
- 8. is it right for a lawyer to tell judge what a prisoners sentence is
- 9. what type of lawyer do i need for a no contact order
- 10. what are the rules in illinios for a lawyer to send solitation notices