What is the fastest way to become a lawyer?
Feb 17, 2022 · How Lengthy Does it Take to Grow to be a Legal professional in the US? The training necessities for turning into a attorney in the US is 7 years. That is damaged down into an undergraduate diploma of 4 (4) years, and a Regulation College diploma of 3 (3) years.
How long does it take to become a successful lawyer?
Nov 02, 2021 · So generally, you’ll take 7 to 8 years to become a lawyer in the USA. 8 years, if you add the additional months for practicing for the bar exams and passing your State’s Bar Association’s character and fitness review. How Long Does it Take to Become a Lawyer in the UK?
What to know before becoming a lawyer?
Feb 23, 2021 · It usually takes seven years to become a lawyer, including four years of undergraduate study and three years of law school. However, many people choose to get a job in the legal field before applying to law school in order to strengthen their application.
How long do you have to go to University for to be a lawyer?
Law students are required by most law schools to complete the law program in three years. Under special circumstances, an extension may be permitted but that is not the norm. Taking all the above factors into account, the shortest path to law school is approximately six years.
How long does it take to become a lawyer?
It takes 7 years to become a lawyer, but that is mostly in the USA. In the UK, it will take you 6 to 7 years to become a Solicitor and 5 years to b...
How many years is law school to be a lawyer?
In the USA, law school takes 3 years for full-time education and 4 years for part-time education. But the part-time path is not common. In the UK,...
What degree do you need to be a lawyer?
To become a lawyer in the USA, you need any kind of undergraduate degree and a Juris Doctor (J.D). In the UK, however, you'll need a Bachelor of La...
What subjects do you need to become a lawyer?
To become a lawyer your undergraduate degree should have covered subjects in English, Public Speaking, Government, History, Economics, and Mathemat...
What do lawyers study?
At law school, lawyers study courses that are fundamental to their law practice. These topics include constitutional law, tort, contracts, property...
What undergraduate degree do you need to be a lawyer?
To become a lawyer in the USA, you need an undergraduate degree in any area of study. But based on your area of specialization, a specific kind of...
How long does it take to become a lawyer?
It usually takes seven years to become a lawyer, including four years of undergraduate study and three years of law school. However, many people choose to get a job in the legal field before applying to law school in order to strengthen their application. Working as a paralegal or legal secretary can provide valuable experience ...
What is a lawyer?
A lawyer provides legal advice to clients, represents them in legal proceedings and creates legal documents. They regularly interpret the law based on the specific situations of their clients. Lawyers also do regular research into current laws and common legal issues. Lawyers can specialize in many areas, including personal injury, immigration, ...
Why is the LSAT important?
Although your LSAT scores are not the only important part of your application, it is important to begin studying and preparing far in advance of your test. High LSAT scores can help law schools identify top applicants. 3.
What is the bar exam?
The bar exam determines if you have all the knowledge and skills to practice law. This usually involves several months of studying for the test, then a character examination and an extensive background check. 5. Apply for jobs.
How do I choose a law school?
Selecting a law school should be a personal decision based on your goals and ideal lifestyle. If possible, ask current law students and alumni at each school about their experiences. Consider the law school's reputation as well as the type of courses they offer.
What to do after passing bar exam?
Once you have passed the bar exam and are certified to practice law, you should focus on applying for jobs at law firms or offices. Lawyers can work with the government, private practices, non-profits and many other organizations.
Do lawyers work full time?
Most lawyers work full time as an employee of a law office or a business's legal department. Salaries for lawyers can be influenced by many factors, including education, experience, location and specialization. Many lawyers work overtime in order to provide the best services to their clients, which can increase pay.
How long does it take to get into law school?
Law school programs are typically three years. Unlike a student's undergraduate degree, law school does not allow a student to choose their own pace. Law students are required by most law schools to complete the law program in three years. Under special circumstances, an extension may be permitted but that is not the norm.
How long does it take to get a bachelor's degree?
On average, earning a bachelor's degree will take approximately two and a half to five years, allowing for full-time attendance. Once a student completes their bachelors, the next phase is taking the LSAT test and gaining acceptance into a law program.
How long does it take to become a lawyer?
How Long Does It Takes to Become a Lawyer? Most people who pursue a career as a lawyer generally take the traditional path of earning a bachelor’s degree followed by three years of law school.
How long does it take to get into law school?
Going to Law School. If you’re able to enroll in law school as a full-time student, you can expect to complete the program in three years. Attending law school on a part-time basis is an option at many law schools, but it does mean you’ll be studying for four rather than three years.
What is the LSAT test?
Your score on the LSAT is a significant part of your law school applications and you’ll need to spend time preparing for it. However, students who are pursuing an undergraduate degree usually complete the test while in college – so preparing for the LSAT doesn’t normally require additional time. If you’re unhappy with your initial score or you already completed your bachelor’s degree, retaking the test or finding time to study for it can increase the amount of time it takes you to become a lawyer.
What is the first step to becoming a lawyer?
Lawyer Education. A bachelors degree will be your first step. There are pre-law degrees along with online legal studies programs. Or view ABA accredited universities. The State Bar Exam. The bar exam is the next step to become a lawyer. The state bar exam will determine whether a person is qualified to practice law in a geographic jurisdiction.
How much do lawyers make in a year?
As of May 2019, lawyers in the United States averaged $122,960 per year. However, this comfortable salary does not come easily. Becoming a lawyer in any jurisdiction requires years of undergraduate and graduate education, passing challenging examinations, and maintaining licensure through continuing education.
What majors are required for law school?
However, the ABA suggests certain undergraduate majors over others, such as English, history, political science, philosophy, business, or economics.
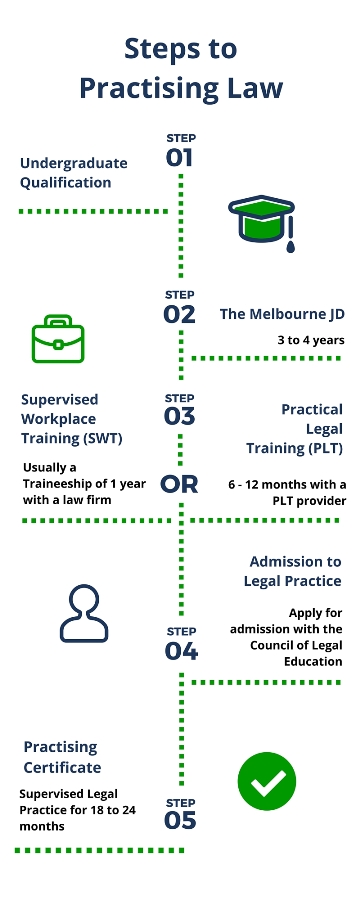
Undergraduate Degree Length and Law School Admission
- Aspiring attorneys will first need to earn a bachelor's degree to get into law school, which typically takes around four years. There's no required field for this bachelor's degree, but some fields are a natural precursor to law school: 1. Philosophy 2. Political Science 3. Economics 4. History 5. Bus…
How Many Years Is Law School?
- Law school students can expect to spend about three years earning a Juris Doctor degree. During the first year of study, classes cover foundational aspects of the field including: 1. Criminal law 2. Civil law 3. Torts 4. Contracts 5. Property law 6. Constitutional law In addition to these core classes, most law programs feature electives that allow students to develop expertise in an are…
Licensure
- After graduating from law school, prospective lawyers need to pass their state's bar exam. Although requirements vary by state, many states require the standardized Multistate Bar Examination. This test contains 200 questions on foundational topics like contracts, criminal law, and torts. States also often require essays on legal topics. The process of taking the bar exam u…
Salary and Job Outlook
- According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, the median salary for lawyers was $120,910 in May 2018. Lawyers earning in the highest 10% had salaries of $208,000 or more per year while salaries for the lowest 10% of earners were $58,220 or less. The BLS predicts that employment opportunities for lawyers will grow by about six percent between 2018 and 2028. This rate is slig…
Popular Posts:
- 1. who pays for the defense lawyer for catholic priests
- 2. how to be a lawyer and travel
- 3. how to file a complaint against your lawyer ohio
- 4. what happened to lawyer ratingz website
- 5. how much money did freddy grays familys lawyer get
- 6. when a lawyer asks you to work without a bond
- 7. what is a rate charged by medical offices for records to a lawyer office in wisconsin
- 8. what is patent lawyer
- 9. what makes a great divorce lawyer
- 10. what is retainer for lawyer